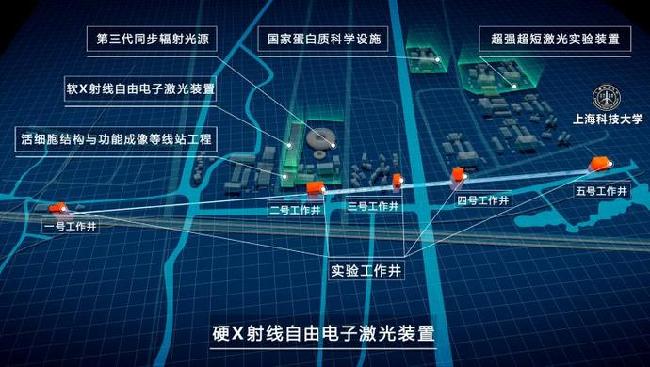
[China Instrument Network Instrument Development] Recently, Shanghai Zhangjiang Comprehensive National Science Center, another major device project - "hard X-ray free electron laser device" has recently been approved to start. This project is the largest major science and technology infrastructure project ever invested by the country as the "13th Five-Year Plan for National Major Science and Technology Infrastructure Construction". It is under the joint care and support of the National Development and Reform Commission, Shanghai Municipality and the Chinese Academy of Sciences. With the joint efforts of all participating units, the phased results started in the year when the project was established.
Picture from Shangguan News
Shanghai University of Science and Technology is the legal entity of the project. The Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences are the joint construction units of the project. The civil engineering project was designed by the Shanghai Tunnel Engineering Rail Transit Design and Research Institute of Shanghai Shentong Group and the Shanghai Architectural Design and Research Institute Co., Ltd. of China Construction Group.
After the device is completed, it will become one of the most efficient and advanced free electron laser user devices in the world, providing high-resolution imaging, ultra-fast process exploration, and advanced technology for multiple disciplines such as physics, chemistry, life sciences, materials science, and energy science. Structural analysis and other cutting-edge research methods form a unique and multidisciplinary scientific research platform. At the same time, the Zhangjiang region will also become an international photonics scientific research highland for gathering synchrotron light sources, soft X-ray free electron lasers, hard X-ray free electron lasers, and super-ultra-short lasers in the same area.
What is a free electron laser?
The free electron laser is a large-scale high-tech device that uses relativistic electrons as its medium and coherent electromagnetic radiation as its light-emitting principle. In 1975, the first free electron laser device based on the low-gain oscillator operating mode was born at Stanford University. To date, low gain free electron lasers are still mainly in the infrared wavelength range. Since the 21st century, a new type of free electron laser based on the principle of high-gain amplifier has made a major breakthrough in technology. Free-electron laser has realized the emergence of ultra-high-brightness hard x-rays, and has been applied to the world's most cutting-edge scientific research. Free electron laser with excellent characteristics, including extremely high peak brightness, 8 to 10 orders of magnitude higher than the current best third-generation synchrotron light source; ultra-short pulse length, can reach 1 femtosecond or even shorter ; Excellent coherence; wide wavelength coverage, and continuously adjustable and so on.
Due to its irreplaceable advantages in performance, the free electron laser has been hailed as the fourth generation of advanced light sources. It is a state-of-the-art research platform for exploring natural mysteries and developing new and high technologies, which greatly contributes to solving the most pressing problems facing humankind. Examples include green chemistry, pharmaceutical innovation, clean energy, new materials and information technology, and laboratory astrophysics. So far, all the large-scale free electron laser devices in the world have been built in laboratories that already have a third-generation synchrotron radiation source, thus forming a new generation of photonic science centers.
Soft X-rays and Hard X-rays
In November last year, the Shanghai Applied Physics Soft X-Ray Free Electron Laser User Device at the Chinese Academy of Sciences officially started construction. Soft X-rays (photon energy ~ 1 keV) have an important band called "water window" and are the only "fourth-generation light source" capable of performing non-invasive three-dimensional holographic imaging and microscopic imaging of living living cells. The time accuracy reaches femtosecond level. It is not a "photograph" of biological molecules but a "video".
Utilizing ultra-high brightness, ultra-fast femtosecond pulse of 1 angstrom wavelength and coherent characteristics, hard X-ray (photon energy ~10kev) free electron laser provides a revolutionary research platform for a wide range of scientific and technological fields, such as high efficiency. High-resolution microscopic images of various materials at the atomic level; ultra-fast movements of femtoseconds and even subseconds of detectable substances; observations of extreme phenomena of high temperature, high pressure, and high energy density in astronomy, plasma science, and basic physics.
(Original Title: “Hard X-Ray Free Electron Laser Device†has been approved for launching the largest investment in major science and technology infrastructure projects so far in China)
Welding Consumables
Fe-Cr-Mo-B Welding Electrodes is a graphite type surfacing electrode, the surfacing metal is molybdenum chromium boron alloy, the hardness of the surfacing layer is HRC=60~65°, and the matrix is Cr7Mo6B8 dispersion hardening and toughening austenite. The surfacing metal is eutectic or near-eutectic alloy, the electrode not only has high temperature resistance (up to 650 ℃) but also wear resistance, toughness and crack resistance. Has high resistance to impact abrasive wear.

It is suitable for surfacing welding of wear-resistant parts in various industries such as steel mills, power plants, cement plants, casting plants, building materials plants, etc., and its welding life is 6~8 times higher than that of other materials.
Welding Rods are classified by use
1. Structural steel electrodes: including carbon steel electrodes and some low alloy steel electrodes
2. Chrome-Molybdenum Welding Electrodes: the weld metal of this type of electrode has different degrees of high temperature resistance.
3. Stainless steel electrode: The weld metal of this type of electrode has different degrees of anti-atmospheric or corrosion-resistant working ability at normal temperature, high temperature or low temperature.
4. Surfacing electrode: The surfacing layer of the weld metal surface of this type of electrode has different degrees of wear-resistant or corrosion-resistant working ability at room temperature or high temperature.
5. AWS E6013 Carbon Steel Welding Rod Welding Electrode: The weld metal of this type of electrode has a certain low temperature resistance working ability.
6. Cast Tungsten Carbide Tube Welding Rod: This type of electrode is used for welding or repairing cast iron.
7. Nickel and nickel alloy electrodes: This type of electrode is used for welding of nickel and nickel alloys, as well as for welding and surfacing of dissimilar metals.
8. Copper and copper alloy electrodes: This type of electrode is used for the welding of copper and copper alloys, as well as for the welding and surfacing of dissimilar metals, and the welding repair of cast iron.
9. Aluminum and aluminum alloy electrodes: These electrodes are used for welding, repairing and surfacing of aluminum and aluminum alloys.
10. Tungsten Carbide Tube Welding Rod Electrode